Misinformation Detection in Mobile Social Networks: A Deep Dive into BERT-LSTM Hybrid Model
The proliferation of misinformation within mobile social networks poses a significant threat to societal discourse and informed decision-making. Traditional methods for detecting misinformation often fall short, struggling to keep pace with the rapid spread of false narratives and the evolving tactics employed by purveyors of fake news. This research explores the potential of a novel approach, a BERT-LSTM hybrid model, to address the challenges of misinformation detection, particularly in the context of mobile social networks where rapid dissemination and limited user engagement data often hinder early identification.
The BERT-LSTM model combines the strengths of two powerful deep learning architectures: Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT) and Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks. BERT excels at capturing contextual nuances within text, allowing the model to understand the subtle meanings and relationships between words. LSTM networks, on the other hand, are adept at processing sequential data, making them ideal for analyzing the temporal dynamics of text, such as the unfolding of a narrative or the progression of an argument. This combination allows the hybrid model to analyze both the meaning and the temporal flow of information within social media content, offering a more comprehensive approach to misinformation detection.
A key challenge in addressing misinformation is the need for early detection. The rapid spread of false narratives necessitates swift identification to mitigate potential harm. Traditional methods often rely on user engagement metrics, such as likes, shares, and comments, to identify potentially misleading content. However, in the early stages of propagation, these metrics are often unavailable or insufficient. This research investigates the ability of the BERT-LSTM model to achieve high accuracy in early-stage detection, even in the absence of user engagement data. The hypothesis is that the model’s deep linguistic and sequential processing capabilities can compensate for the lack of user feedback, allowing it to identify misinformation based solely on the textual content.
Beyond detection, this research also explores the potential of the BERT-LSTM model as an educational tool for enhancing digital literacy. By providing insights into the linguistic and structural characteristics of misinformation, the model can be used to develop training programs and educational applications that empower users to critically evaluate online content. This approach aims to foster critical thinking skills and enhance individuals’ ability to discern credible information from falsehoods, contributing to a more informed and resilient online community.
The research utilizes a custom-built web crawler to collect a diverse dataset of social media content, primarily from Twitter, labeled as either misinformation or genuine information. This dataset includes both English and Chinese text, allowing for cross-linguistic analysis and the identification of language-specific patterns in misinformation. The data undergoes meticulous preprocessing and feature engineering, including tokenization, stop word removal, and the extraction of features such as polarity and comment length. This prepared data is then used to train and evaluate the performance of the BERT-LSTM model.
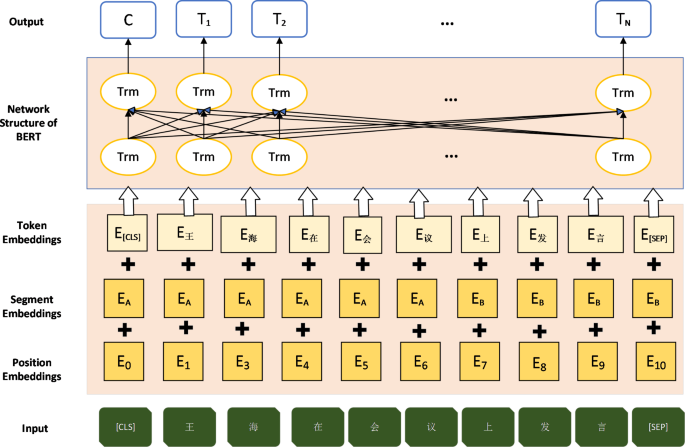
The architecture of the BERT-LSTM model involves several key stages. First, the input text is tokenized and embedded into a high-dimensional vector space. These embeddings are then fed into the BERT layer, which utilizes transformer layers and self-attention mechanisms to capture the contextual meaning of each token. The output of the BERT layer is a sequence of contextualized embeddings, which are then passed to the LSTM layer. The LSTM network processes these embeddings sequentially, capturing the temporal dependencies within the text. Finally, a fully connected layer and a softmax layer produce the final prediction, classifying the content as either misinformation or genuine information.
The research compares the performance of the BERT-LSTM model against traditional machine learning models, such as Naive Bayes and Support Vector Machines (SVM), and other state-of-the-art deep learning architectures, including Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs). The goal is to evaluate the efficacy of the hybrid model and determine whether its unique combination of contextual and sequential processing leads to improved accuracy in misinformation detection.
The research aims to address three core questions: How does the BERT-LSTM model compare to existing methods in terms of accuracy? Can it effectively detect misinformation in the early stages, without relying on user engagement data? And finally, how can this model be leveraged as an educational tool to enhance digital literacy? By answering these questions, this research seeks to contribute to the development of more effective strategies for combating misinformation and promoting a more informed and discerning online environment. The findings are expected to have significant implications for individuals, social media platforms, and policymakers alike, empowering them to address the challenges of misinformation in the digital age.