The Rise of Social Media and the Spread of Fake News
Over the past decade, online social networks (OSNs) like Twitter, Facebook, and Instagram have revolutionized how we consume news. These platforms have largely eclipsed traditional print media, becoming primary sources of information and daily updates. This shift has empowered individuals to connect and share information readily, democratizing news dissemination in unprecedented ways. However, this rapid evolution has also opened the door to a concerning phenomenon: the proliferation of fake news. Initially designed for social interaction, OSNs have morphed into powerful news distribution channels, making them fertile ground for misinformation and disinformation campaigns.
The COVID-19 pandemic further intensified this trend. As the world grappled with uncertainty, people flocked to OSNs for updates, creating a perfect storm for the spread of false information. The urgency of the situation, coupled with the sheer volume of information circulating online, made it increasingly difficult to distinguish between credible news and fabricated stories. This influx of misinformation, intentionally or unintentionally shared, has significant real-world consequences, impacting public health decisions, political discourse, and social cohesion.
Combating Fake News: A Technological Challenge
Recognizing the gravity of this issue, researchers have been actively developing tools to detect and combat fake news. Machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) have emerged as promising technologies in this fight. However, existing solutions often fall short. Many studies rely on pre-labeled datasets, focusing primarily on algorithm performance rather than real-world application and user experience. These approaches often use smaller datasets due to computational limitations and typically address only a single aspect of fake news, such as propaganda or satire, rather than providing a comprehensive categorization.
Furthermore, traditional fact-checking methods, often employed by specialized websites, rely on manual verification by human experts. While valuable, these approaches are time-consuming, expensive, and cannot scale to address the sheer volume of information circulating on OSNs. The subjective nature of human analysis can also introduce bias, further complicating the process.
Introducing FANDC: A Cloud-Based Solution for Real-Time Fake News Detection
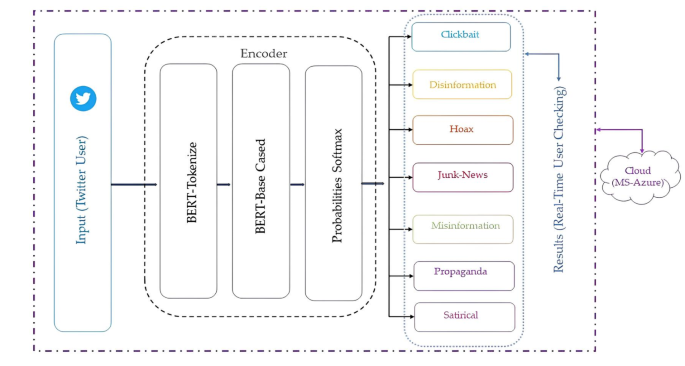
To address these limitations, a new system called Fake News Detection on Cloud (FANDC) has been developed. This cloud-based platform utilizes the Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT) algorithm, a powerful NLP tool, to detect fake news in real-time and categorize it into seven distinct subcategories: clickbait, disinformation, hoaxes, junk news, misinformation, propaganda, and satire. This granular approach provides users with more detailed insights into the nature of the content they encounter, empowering them to make informed decisions.
Unlike previous research, FANDC utilizes a large, system-specific corpus and leverages the power of cloud computing, making it more robust and secure against cyber threats. Its distributed and containerized architecture enhances resilience and scalability. The system offers a user-friendly interface, providing real-time feedback directly within the OSN environment, making it a practical tool for everyday users.
Research Questions and Methodology
The central research questions driving the development of FANDC are:
- Can the developed system detect fake news spread on OSNs online and in real-time?
- Can the developed system categorize fake news spread in OSNs?
To answer these questions, the study follows the CRISP-DM (Cross-Industry Standard Process for Data Mining) methodology. This structured approach guides the data acquisition, pre-processing, categorization, and system design processes. The study also defines specific evaluation criteria to assess the system’s performance.
Bridging the Gap in Existing Research
FANDC represents a significant advancement in the fight against fake news. It addresses the identified gap in the literature by providing a real-time, categorized detection system that operates within the OSN environment. This contrasts with previous studies that often focused on offline analysis or provided general fake news detection without categorization. The cloud-based architecture ensures scalability, reliability, and accessibility, making it a practical solution for a wide range of users. Furthermore, the use of a large, system-specific corpus enhances the system’s accuracy and robustness.
The Importance of Real-Time, Categorized Detection
The ability to detect and categorize fake news in real-time is crucial in today’s information landscape. Providing users with immediate feedback empowers them to evaluate the credibility of news content before sharing it, thereby stemming the tide of misinformation. The categorization feature further enhances user understanding by providing context and insights into the nature of the potentially fake news. This approach promotes media literacy and empowers individuals to navigate the complex world of online information more effectively. By integrating seamlessly with existing OSN platforms, FANDC offers a practical and user-friendly solution to a pressing global challenge.