AI Together: Reducing Interval Breast Cancer Rates Through Artificial Intelligence in Digital Breast Tomosynthesis (DBT) Exams
Manisha Bahl, MD, along with her team from Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, has made a significant contribution to the field of breast cancer detection by exploring the potential of artificial intelligence (AI) in enhancing the accuracy of digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) exams. In a groundbreaking study published on July 29, 2023, the team reported that AI could significantly improve the localization of interval breast cancers at screening DBT exams, ultimately reducing false-negative rates and improving patient outcomes.
In their investigation, the AI model, Insights DBT, was trained to accurately localize interval breast cancers on retrospective CAD scans. The team found that, on average, the AI correctly identified approximately 33% of interval cancers at screening DBT exams during a 5-year follow-up period (2011–2023). This represents a meaningful enhancement over manual screening methods, as manual positivity rates typically fall near the threshold of false-negative rates. The findings highlight the importance of leveraging advanced technology to further refine and optimize breast cancer screening practices.
The study also made a critical assessment of why existing DBT practices are not enough to reduce false-negative rates. The team explained that while DBT exams can improve radiologist diagnostic accuracy during screening, additional efforts are needed to minimize false negatives. They emphasized the role of AI in addressing this gap by introducing more specific localization and categorization criteria, thereby decreasing the proportion of undiagnosed cancers.
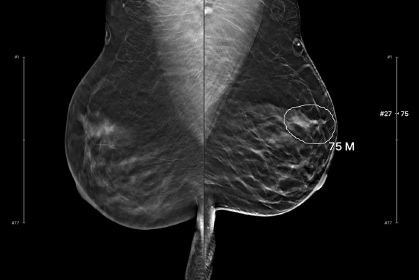
As demonstrated by an illustrative example, a 41-year-old woman presented for a digital breast tomosynthesis exam, with findings interpreted as negative, only to later undergo a grade 3 invasive ductal carcinoma surgery. After a week of IDA tomosynthesis, the radiologist, despite the suspicious lesion observed, agreed to re-diagnose based on the AI’s findings. The AI, marked by high scores in specific clinical orientations (81 on the craniocaudal and 75 on the mediolateral oblique views), precisely localized the structural distortion corresponding to the nas VF cell, which was then diagnosed as an interval cancer.
The study team’s findings were validated by analyzing the AI’s performance across various DBT exam types, including interval, true positive, true negative, and false positive exams. Using standardized score thresholds, the AI accurately identified 73% of interval cancers in 224 women, with an average age of 61 years. For undiagnosed cancers, the lesion size (22–32 mm) and axillary lymph node positivity (21–42.5 mm) emerged as significant predictors of true positive, true negative, and false positive cases, respectively.
The research team also demonstrated the robustness of their approach by applying the same threshold to the AI’s outputs. The AI correctly localized 84.4% of true positive cancers and achieved 85.9% accuracy in identifying true negatives and 73.3% in false positives. These results underscore the high precision of the Insights DBT algorithm in identifying interval cancers, which reduces the overall number of undiagnosed cases.
The article concludes with a))?arcing of the findings to highlight the potential of AI in improving breast cancer screening. While definitive early diagnosis is attainable with DBT, the study suggests that advancements in localization and categorization criteria through AI could significantly lower false-negative rates. This information underscores the importance of collaborating with radiologists and optimizing tomographic algorithms to deliver more accurate and timely mammogram evaluations.
Looking ahead, the study emphasizes the need for prospective trials to further validate AI’s impact on accuracy and fals intercepted risks. Additionally, continuous efforts to refine and customize the AI model must be prioritized to ensure that benefits are leveraged for actual patient care and reduced unnecessary harms in the clinic. These strides could pave the way for more efficient screening practices, ultimately improving patient outcomes and patient satisfaction.