AI-Generated Deepfakes Plague the Sports World, Erode Credibility, and Stoke Fan Emotions
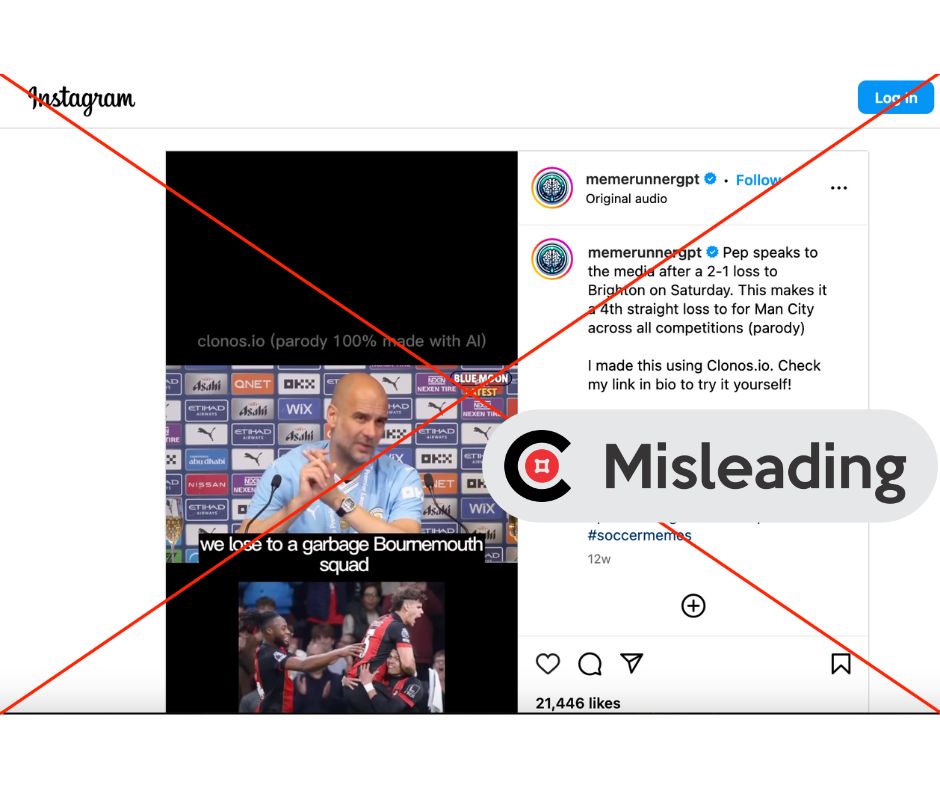
The world of sports journalism is grappling with a new and insidious threat: AI-generated deepfake videos that spread misinformation and manipulate fan emotions. A recent incident involving Manchester City manager Pep Guardiola highlights the growing problem. Following a string of defeats, including a 4-0 thrashing by Tottenham in the Carabao Cup, an Instagram account, @memerunnergpt, posted a fabricated video of Guardiola calling Spurs "garbage" and expressing regret over his contract extension. The video quickly gained traction, despite Guardiola never having made such remarks. This incident underscores the ease with which AI can create convincing yet entirely false narratives, potentially damaging reputations and inflaming fan tensions. @memerunnergpt has a history of similar fabrications, including fake videos of Tottenham manager Ange Postecoglou and Real Madrid manager Carlo Ancelotti.
The proliferation of AI-generated misinformation is not limited to football. Another account shared a fabricated video of Manchester United manager Ruben Amorim criticizing the signing of goalkeeper Andre Onana after a defeat. The video garnered thousands of reposts and likes on X (formerly Twitter), demonstrating the viral potential of such content and its capacity to reach a wide audience. Research from the University of Limpopo in South Africa confirms that fake sports news is a pervasive problem on social media, jeopardizing journalistic integrity and credibility. Sensationalized false narratives force legitimate news outlets to compete for attention using similar tactics, further degrading the quality of sports reporting.
Sports analysts and fact-checkers warn that this trend poses a serious threat to the credibility of sports journalism and fan engagement. Dotun Omisakin, a sports analyst, emphasizes the unregulated nature of social media and the ease with which AI technology can be exploited for malicious purposes. Sport, by its very nature, evokes strong emotions, making fans particularly vulnerable to manipulative content, especially during periods of team struggles. False narratives can exacerbate existing tensions and lead to irrational reactions from fans.
The impact of misinformation extends beyond fans to players, coaches, and teams. Omisakin cites examples of players like Victor Osimhen whose performances have been unfairly scrutinized due to misleading headlines, potentially impacting their morale and confidence. He also points to instances where fabricated reports have created friction between players and coaches, leading to conflicts and resignations. Omisakin stresses the need for stricter regulations and penalties to combat the spread of AI-generated misinformation in sports.
Caleb Ijioma, a disinformation analyst, highlights the potential for deepfakes to depict athletes and coaches in compromising situations, damaging their reputations and misleading fans. He references the "Synthetic Echo" ring, a network of sports news websites using AI-generated content to deceive readers and generate advertising revenue. Ijioma warns of the dangers of fabricated images depicting on-field violence, which could incite real-world violence among fans. He recommends using online tools to identify AI-generated content and advises caution with newly created accounts and websites.
Ijioma also addresses the issue of transparency surrounding AI-generated content. While transparency is generally considered positive, disclosing AI involvement can sometimes backfire, leading to audience distrust. He advises media platforms to clearly label AI-generated content and emphasizes the importance of not over-relying on AI for content creation. Ijioma also encourages journalists to adopt a critical mindset, identifying potential gaps in reporting that misinformation agents might exploit.
Combating misinformation requires a multi-pronged approach involving sports organizations, media outlets, and technology companies. Ijioma recommends that sports organizations establish official channels for updates, engage with fans on social media, and promote critical thinking. He also stresses the importance of collaboration between sports organizations and media outlets to quickly address false information. Phillip Anjorin, a fact-checker, underscores the threat posed by deepfakes, especially in regions with low levels of digital and media literacy. He encourages individuals to be vigilant, identify inconsistencies in visuals and audio, and utilize verification tools.
Anjorin calls for a collaborative effort involving individuals, sports organizations, and tech companies. He encourages individuals to verify questionable content using tools like Google Images. He recommends that sports organizations use AI to monitor social media for misinformation and threats against players. He also calls on technology companies to be more transparent about their AI tools and collaborate with fact-checkers to improve detection mechanisms. Education and media literacy campaigns are crucial to empowering individuals to identify and resist misinformation. The fight against AI-generated deepfakes requires a collective effort to preserve the integrity of sports journalism and protect fans from manipulation.