The Spread of Fake News in 2017: A Deep Dive into Traffic Sources and the Importance of Media Literacy
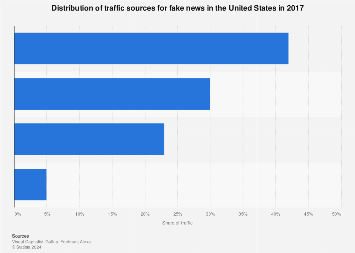
The year 2017 witnessed a surge in the spread of fake news, raising significant concerns about the impact of misinformation on public discourse and democratic processes. Understanding the sources of this deceptive content is crucial for combating its proliferation. A Statista report, based on data from Visual Capitalist, offers valuable insights into the distribution of traffic sources for fake news in the United States during that year. This analysis delves into the various channels through which fake news reached consumers, shedding light on the digital landscape that facilitated its dissemination.
Social Media’s Role in the Dissemination of Fake News
The Statista data reveals that social media platforms played a dominant role in driving traffic to fake news websites. Facebook, in particular, emerged as a primary source, accounting for a significant portion of overall traffic. This finding underscores the power of social media algorithms in shaping information consumption patterns and highlights the potential for these platforms to be exploited for the spread of misinformation. The virality of fake news on social media can be attributed to several factors, including the personalized nature of news feeds, the prevalence of echo chambers, and the ease with which fabricated content can be shared and amplified.
Search Engines and the Visibility of Fake News
Search engines also contributed to the visibility of fake news, albeit to a lesser extent than social media. This suggests that individuals actively seeking information online may have inadvertently encountered fake news through search results. The role of search engine algorithms in prioritizing certain websites and content raises questions about the potential for biased or manipulated search results to influence public perception. This highlights the need for search engines to refine their algorithms to effectively filter out misleading information and promote credible sources.
Direct Traffic and the Role of Existing Networks
A notable portion of traffic to fake news websites came from direct sources, indicating that individuals were either accessing these sites through bookmarks or directly typing the URLs into their browsers. This suggests the existence of established networks or communities that actively sought out and consumed fake news. This direct access may reflect a pre-existing inclination towards certain narratives, potentially within echo chambers or closed online groups.
The Importance of Media Literacy and Critical Thinking
The findings from Statista underscore the urgent need for improved media literacy and critical thinking skills among online users. As fake news becomes increasingly sophisticated and difficult to distinguish from credible sources, individuals must be equipped with the tools to evaluate information critically. This includes verifying sources, cross-checking facts, and being aware of potential biases. Educational initiatives and public awareness campaigns can play a vital role in promoting media literacy and empowering individuals to navigate the complex digital landscape.
The Responsibility of Tech Companies and Policymakers
Addressing the spread of fake news requires a multi-faceted approach involving tech companies, policymakers, and individuals. Social media platforms and search engines bear a responsibility to implement measures to combat the spread of misinformation on their platforms. This includes improving algorithms to identify and flag fake news, promoting credible sources, and providing users with tools to report misleading content. Policymakers also have a role to play in regulating online platforms and ensuring accountability without infringing on freedom of speech.
The Ongoing Challenge of Combatting Misinformation
The fight against fake news is an ongoing challenge that requires constant vigilance and adaptation. As technology evolves and new platforms emerge, so too will the tactics used to spread misinformation. Continued research, collaboration, and a commitment to truth and accuracy are essential to safeguarding the integrity of information and protecting democratic processes. The Statista data provides a valuable snapshot of the fake news landscape in 2017, serving as a reminder of the importance of critical thinking and media literacy in the digital age. Understanding the patterns and sources of fake news empowers individuals and institutions to better address this evolving threat to informed public discourse.