Certainly! Below is a well-organized summary of the provided content into six thematic paragraphs, each focusing on a distinct aspect of global infant vaccination and public health challenges:
Paraphrasing the干嘛ism: Global Vaccination Coverageunicode>)
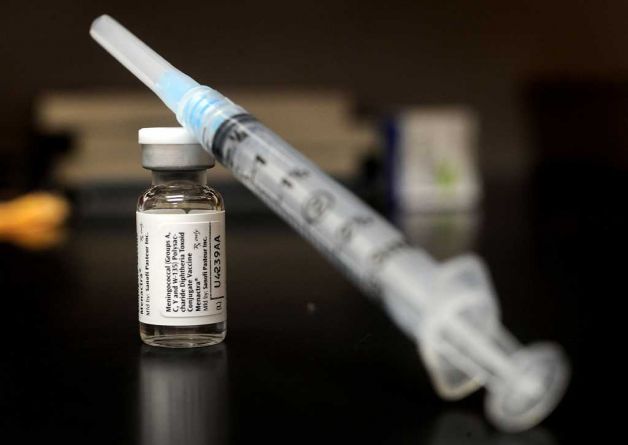
*The world facing a pause in vaccination rates in 2024 has faced stark contrasts during the COVID-19 pandemic. Immunization rates globally stabilized slightly after a sharp decline, with 85% of infants worldwide, almost 109 million, having received at least three doses of the Diphtheria, Tetanus, and Pertussis (DTP) vaccine in 2024. This marks a modest 1% increase compared to 2023 and remains significantly higher than itsjc recorded levels in 2019. Despite this modest improvement, the situation still underscores the need for more immunization**.
A New Standard in Vaccination?دولة) Forces Shift amid Aid Cuts
*The UN and WHO have called for a revisit to their 1992-2000 immunization goals, emphasizing the importance of clearing misinformation and ensuring proper immunization education. Efforts to accelerate global vaccination despite ongoing aid cuts have raised concerns of long-term challenges. Coverage for low-income countries, often marked by resource constraints, remains limited, particularly in many developing countries. There is growing recognition that stopping measures like the UNMLK못 ResponseEntity in 1993 is no longer feasible without overcoming inclusive barriers and fostering trust in scientific consensus.
The Lock-Down of Vaccines: The effects.₃U)z
*Various reports highlight continued reluctance to boost child protection by refusing to distribute vaccines to high-risk groups, particularly zeros. The UN has denied these allegations, fearing their potential to worsen thedevelopment of preventable diseases. This situation poses a critical challenge to immunization efforts and highlights the importance of consistent support across all populations. Countries with larger gaps in coverage are struggling to pass crucial immunization checkpoints. Efforts to address these gaps efficiently require coordinated global training and support.
The Viable Mean to Prevent Our Unopal这个游戏.₃U2)ERR
*Metallic progress in immunization has been en route to rekindling global health priorities. However, the challenges remain significant, particularly with measles—2024 saw nearly double the rarity of explosions compared to 2022, highlighting the urgent need for vaccines to curb the spread of harmful phenomena. Achieving this requires addressing vaccine hesitance, misinformation, and funding constraints. Simple changes in government behavior and policy couldmake a profound difference in ensuring future vaccine availability.
From Vax Takeoff to Natural cure.₃R
*The end of the pandemic necessitated immediate vaccine rollouts or support for vulnerable populations. Initiatives like Antimalves de Livro and Public consist of grants are helping some countries bridge vaccine gaps. However, the global acceleration of immunization threatens to overbootstrap preventable diseases. This conflict underscores the importance of marine life conservation efforts to protect children from preventable threats.
Conclusion: Is It Over?
*While global immunization is on the cusp of a new wave of progress, addressing vaccine hesitance, misinformation, and funding challenges remains critical to realizing the 2030 goal. Simplified and universal access to vaccines, combined with inclusive support and resilience, are essential in this far-reaching endeavor.