The Persistent Threat of Fake News: Navigating the Disinformation Landscape
The proliferation of fake news has become a pervasive challenge in the digital age, eroding trust in traditional media and fueling social division. This insidious phenomenon, characterized by the deliberate spread of false or misleading information, has infiltrated every corner of the internet, from social media platforms to seemingly reputable news outlets. Understanding the origins, mechanisms, and impact of fake news is crucial for fostering media literacy and safeguarding democratic processes.
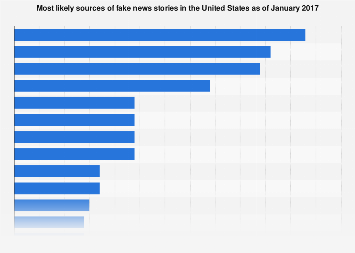
One key aspect of combating fake news is recognizing its various sources. While some purveyors of disinformation are motivated by political agendas or ideological convictions, others seek financial gain through clickbait and sensationalized content. Disentangling these motives and identifying the sources behind fake news stories is essential for holding them accountable and minimizing their influence. This often requires a combination of investigative journalism, fact-checking initiatives, and technological solutions aimed at identifying and flagging false information.
The accessibility of online platforms has amplified the reach of fake news, enabling it to spread rapidly and widely. Social media algorithms, designed to maximize engagement, can inadvertently prioritize sensational content, regardless of its veracity. This creates echo chambers where users are primarily exposed to information that confirms their existing biases, further entrenching their beliefs and making them more susceptible to manipulation.
The consequences of fake news extend far beyond individual misinformation. It can undermine public trust in institutions, erode social cohesion, and even influence political outcomes. The 2016 US presidential election serves as a stark reminder of the potential impact of disinformation campaigns on democratic processes. Foreign interference, coupled with the viral spread of fake news on social media, raised serious concerns about the integrity of the electoral system.
Combating the spread of fake news requires a multi-pronged approach. Media literacy education plays a vital role in empowering individuals to critically evaluate information and identify potentially misleading content. This involves developing skills in source verification, fact-checking, and recognizing common tactics used in disinformation campaigns. Furthermore, encouraging healthy skepticism and promoting lateral reading – the practice of cross-referencing information with multiple sources – can help individuals navigate the complex online landscape.
Technological solutions also offer promising avenues for addressing the challenge of fake news. Artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms can be trained to identify patterns and markers of disinformation, flagging potentially false content for further review. Fact-checking organizations leverage these technologies to streamline their efforts and debunk false claims more efficiently. However, it is important to acknowledge the limitations of these technologies and the potential for biases in their design and implementation. Human oversight remains crucial in ensuring accuracy and preventing censorship.
The Role of Individuals in Combating Fake News
Individuals play a crucial role in stemming the tide of fake news. By adopting responsible online behavior, they can contribute to a more informed and trustworthy information ecosystem. This includes verifying information before sharing it, avoiding the spread of unsubstantiated rumors, and reporting suspicious content to platform administrators. Furthermore, engaging in respectful dialogue and challenging misinformation with factual evidence can help to counter the spread of false narratives.
The Responsibility of Social Media Platforms
Social media platforms bear a significant responsibility in addressing the proliferation of fake news on their platforms. They must invest in robust content moderation systems, prioritize transparency in their algorithms, and collaborate with fact-checking organizations to identify and flag misleading information. Furthermore, they should empower users with tools and resources to report fake news and access credible information.
The Importance of Media Literacy Education
Media literacy education is essential for equipping individuals with the skills to navigate the complex information landscape and critically evaluate the credibility of sources. Educational institutions, community organizations, and government agencies should prioritize media literacy programs that teach individuals how to identify fake news, understand its impact, and engage responsibly with online content.
The Role of Journalists and News Organizations
Journalists and news organizations play a vital role in upholding journalistic integrity and combating the spread of misinformation. They must adhere to rigorous ethical standards, prioritize accuracy and fairness in their reporting, and actively debunk false claims. Furthermore, they should invest in investigative journalism to expose the sources and mechanisms behind disinformation campaigns.
The Need for International Collaboration
The fight against fake news requires international collaboration. Governments, international organizations, and civil society groups must work together to develop shared strategies, share best practices, and coordinate efforts to combat the spread of disinformation across borders. This includes addressing the issue of foreign interference in elections and promoting cross-border cooperation in fact-checking and media literacy initiatives.
In conclusion, addressing the challenge of fake news requires a collective effort. Individuals, social media platforms, journalists, educators, and policymakers must all play their part in fostering a more informed and resilient information ecosystem. By promoting media literacy, investing in technological solutions, and upholding ethical standards, we can collectively work towards mitigating the harmful impact of fake news and safeguarding the integrity of our democratic societies.